MULTIPURPOSE INTERNET MAIL EXTENSIONS (MIME)
· Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is a supplementary protocol that allows the non-ASCII data such as picture, images and video/audio content to be sent through e-mail.
· MIME was invented to overcome the following limitations of SMTP:
1. SMTP cannot transfer executable files and binary objects.
2. SMTP cannot transmit text data of other language, e.g. French, Japanese, Chinese etc. as these are represented in 8-bit codes.
3. SMTP services may reject mails having size greater than a certain size.
4. SMTP cannot handle non-textual data such as pictures, images, and IP services may reject mails having size greater than a certain size video/audio content.
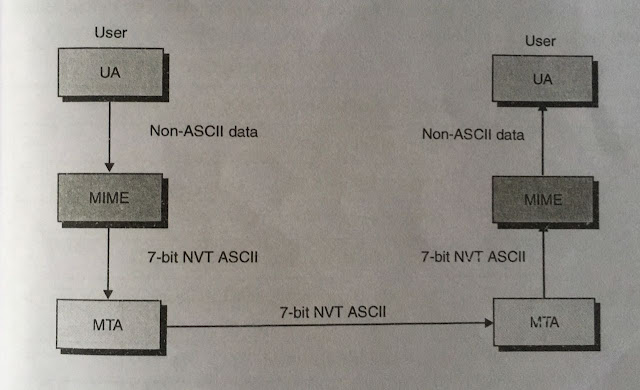
· MIME transforms non-ASCII data at sender site to NVT ASCII data and delivers them to client MTA so that it can be sent through internet. This message is then transformed into its original form at the receiver site. (see fig.).
· Therefore MIME is a set of software functions that transforms non-ASCI data to ASCII data.
· The MIME specification includes the following elements:
1. Message header fields. Five message header fields are defined. These fields provide information about the body of the message.
2. Content formats. A number of content formats are defined, thus standardizing representations that support multimedia electronic mail.
3. Transfer encoding. Transfer encoding are defined that enable the conversion of any content format into a form that is protected from alteration by the mail system.
MIME Header
The five header fields defined in MIME are as follows:
1. MIME-version. It indicates the MIME version being used. The current version is 1.1. It is represented as : MIME-version: 1.1.
2. Content-type. It describes the type and subtype of the data in the body of the message. The content type and content subtype are separated by slash. This field describes how the object in the body is to be interpreted. The default value is plaintext in US ASCII. Content type field is represented as:
Context-type: <type/subtype; parameters>
There are seven different types and fourteen sub-types of content.
Type | Sub-type | Description | ||||||||
Text | Plain | Uniformatted text in US ASCII or ISO 8859 | ||||||||
Image |
|
| ||||||||
Video | Mpeg | MPEG format | ||||||||
Audio | Basic | Single channel encoding of voice at 8 KHz. | ||||||||
Message | Rfc822 | The body is an encapsulated messafe that confirms to RFC 822. | ||||||||
|
| |||||||||
Multipart |
|
| ||||||||
Application |
|
|
3. Content-transfer encoding. it describes how the object within the body has been encoded to US ASCII to make it acceptable for mail transfer. Thus it specifies the method used to encode the message into Os and 1s for transport. The content transfer encoding field is represented as:
Content-transfer-encoding : <type>
The various encoding methods used are given in the table below
Type | Description |
7 bit | The body contains the 7 bit ASCII characters with maximum length 1000 characters. |
8 bit | There can be non ASCII 8 bit characters but the maximum length of the body is limited to 1000 characters/ |
Binary | Binary 8 bit characters without limitation of 1000 characters in the body. |
Quoted printable | This is usefil when data consists of largely printable characters. Characters in the range decimal equivalent 33 to 61 in ASCII are represented in ASCII. Others are represented as two-digit hex representation preceeded by ‘=’ sign. Non-text characters are replaced with six digit hex sequence. |
Base 64 | 6 bit block of input data is encoded into 8 bit block of output. |
4. Content-Id. It is used to uniquely identify the MIME entities in multiple contexts i.e. it uniquely identifies the whole message in a multiple- message environment. This field is represented as
Content-id: id <content-id>
5. Content-description. It is a plaintext description of the object within the body. It specifies whether the body is image, audio or video. This field is represented as:
Content-description: <description>
The various fields in the MIME header are shown in the figure.











No comments:
Post a Comment